Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition that affects how a person thinks, interacts, and experiences the world. It is called a "spectrum" because it manifests in a wide range of behaviors and symptoms, with varying levels of severity. Individuals with ASD can have different strengths and challenges, and the condition may present in various ways.
Key Characteristics of ASD:
-
Social Communication Challenges:
- Difficulty with verbal and non-verbal communication (e.g., understanding tone, body language, or facial expressions).
- Challenges in developing and maintaining relationships or engaging in social interactions.
- Trouble understanding social cues or responding to others' emotions appropriately.
-
Repetitive Behaviors or Restricted Interests:
- Engaging in repetitive movements, routines, or speech (e.g., hand-flapping, lining up objects).
- Intense focus on specific interests or activities, often to the exclusion of everything else.
- Insistence on sameness or difficulty with changes in routine or environment.
-
Sensory Sensitivities:
- Heightened or diminished sensitivity to sensory inputs, such as lights, sounds, textures, or smells.
-
Difficulty with Adaptive Skills:
- Challenges in daily functioning, including tasks like self-care, organization, or managing changes in the environment.
Diagnosis and Support:
- Early Signs: Often detected in early childhood, with parents noticing delays in speech, social interactions, or behavior.
- Assessment: Diagnosing ASD involves a comprehensive evaluation by a team of professionals, including developmental history, behavioral assessments, and possibly autism-specific diagnostic tools.
- Interventions: There is no "cure" for ASD, but therapies (e.g., speech therapy, occupational therapy, behavioral therapy) can help improve communication, social skills, and adaptive functioning.
The Spectrum:
- People with ASD can have a range of intellectual abilities, from gifted to those with intellectual disabilities.
- Some individuals are non-verbal, while others may have highly developed language skills.
- Each individual with ASD is unique, and their strengths and needs should be addressed on a case-by-case basis.
Common Co-occurring Conditions:
- Anxiety, depression, ADHD, or sensory processing disorder may also be present in individuals with ASD.
Autism therapy procedure
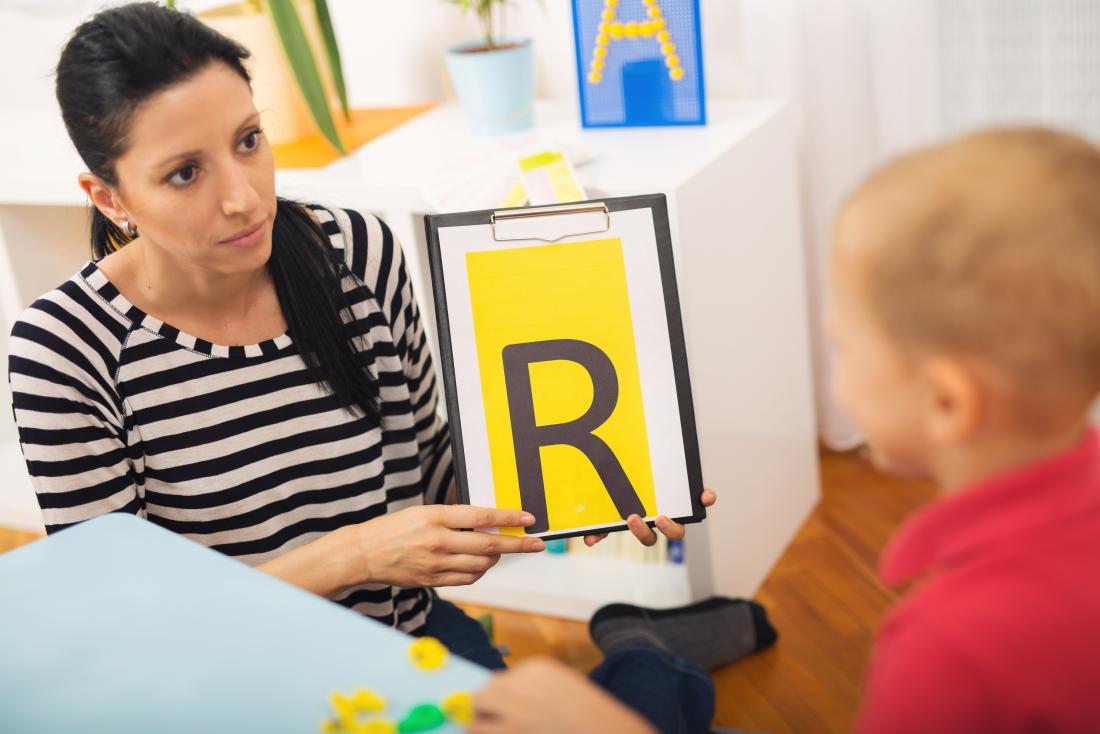
Autism therapy procedures focus on helping individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) improve their social, communication, and behavioral skills while supporting their  unique needs. Therapy is tailored to each individual based on their age, symptoms, strengths, and challenges. Here are the primary types of therapies and procedures commonly used for individuals with autism:
unique needs. Therapy is tailored to each individual based on their age, symptoms, strengths, and challenges. Here are the primary types of therapies and procedures commonly used for individuals with autism:
1. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
ABA is one of the most widely used and researched therapies for ASD. It focuses on understanding and modifying behavior through structured interventions.
- Procedure: ABA therapists break down tasks into small, manageable steps, rewarding positive behaviors and teaching new skills in a systematic way.
- Goal: Increase desirable behaviors (e.g., social skills, communication) and decrease problematic behaviors (e.g., aggression, self-injury).
- Types:
- Discrete Trial Training (DTT): Focuses on teaching specific skills through structured, one-on-one sessions.
- Natural Environment Teaching (NET): Teaches skills in real-life settings, such as at home or in the community.
2. Speech and Language Therapy
Speech therapy helps individuals with ASD improve their communication skills, whether verbal or non-verbal.
- Procedure: Therapists work on building speech and language abilities, improving articulation, and addressing language comprehension issues. They may also use augmentative communication devices if verbal speech is challenging.
- Goal: Enhance both expressive (speaking) and receptive (understanding) language skills, along with social communication abilities like turn-taking and conversational skills.
3. Occupational Therapy (OT)
Occupational therapy focuses on helping individuals with ASD develop the skills needed for daily life and self-care activities.
- Procedure: Occupational therapists use play, routines, and hands-on activities to address sensory processing issues, fine motor skills, and self-regulation.
- Goal: Improve the ability to participate in activities such as dressing, feeding, grooming, and schoolwork.
4. Social Skills Training
Social skills training helps individuals with ASD develop appropriate social behaviors and interactions.
- Procedure: Therapists may use role-playing, video modeling, or social stories to teach social norms, eye contact, conversational turn-taking, and understanding emotional cues.
- Goal: Help individuals form meaningful relationships, understand social rules, and improve their interactions with peers and adults.
5. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is often used for individuals with ASD, especially those who also have co-occurring conditions like anxiety or depression.
- Procedure: CBT involves identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. The therapist works with the individual to develop coping strategies for anxiety, frustration, or other emotional difficulties.
- Goal: Improve emotional regulation, reduce anxiety, and help individuals better understand their feelings and reactions.
6. Sensory Integration Therapy
This therapy helps individuals with ASD who experience sensory processing difficulties (e.g., being overly sensitive to sounds or textures).
- Procedure: Sensory integration therapists provide activities that expose the individual to various sensory experiences in a controlled and structured way.
- Goal: Help individuals tolerate and adapt to sensory stimuli, reducing anxiety or distress related to sensory sensitivities.
7. Developmental, Individual Differences, Relationship-Based (DIR/Floortime)
DIR/Floortime is a therapy approach that focuses on emotional and developmental milestones.
- Procedure: This therapy encourages therapists and parents to engage in play at the child’s developmental level, promoting interaction, emotional connection, and problem-solving.
- Goal: Support emotional and social development by fostering relationships, enhancing emotional expression, and developing communication skills.
8. Parent-Training and Support
Parental involvement is a critical part of therapy. Parent training teaches caregivers how to support the child’s development in day-to-day activities.
- Procedure: Parents learn how to implement strategies at home that reinforce what their child learns in therapy. This might involve managing behavior, setting routines, or encouraging communication.
- Goal: Empower parents to be active participants in their child’s progress and create a supportive home environment.
9. Dietary and Nutritional Support (if applicable)
Some individuals with ASD may have dietary restrictions or sensitivities that impact their behavior.
- Procedure: In some cases, a nutritionist may work with families to address issues like food selectivity or digestive concerns. Specialized diets, like gluten-free or casein-free, might be recommended.
- Goal: Address any nutritional deficiencies, improve eating habits, and reduce any food-related sensitivities or allergies that may contribute to behavior challenges.
10. Medication (when necessary)
While there is no medication that cures ASD, medications may be prescribed to manage certain symptoms or co-occurring conditions such as anxiety, depression, or hyperactivity.
- Procedure: Medication may be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan in combination with behavioral therapies.
- Goal: Reduce behavioral symptoms, manage anxiety or mood disorders, and improve overall quality of life.
General Therapy Procedure:
-
Assessment: A comprehensive evaluation is conducted by a team of professionals to understand the individual's strengths, weaknesses, and needs. This may include observations, interviews, and standardized testing.
-
Individualized Plan: Based on the assessment, a tailored therapy plan is created, outlining specific goals, methods, and timelines for progress.
-
Implementation: Therapy begins with structured sessions, often delivered by specialists (e.g., speech therapists, behavior analysts, or occupational therapists).
-
Review and Adjustment: Regular reviews track progress, and the plan is adjusted as needed based on the individual’s response to therapy.
-
Family Involvement: Therapists often involve family members to ensure consistency of strategies across different settings (home, school, community).